Reducing Legal Immigration Helps US Workers’ Wages
Immigration into the US has increased the supply of labor in the economy. Legalizing illegal aliens and substantial increases in legal immigration has considerably increased the supply of labor to the US employers. Economic theory of labor supply and demand suggests that any increase in the supply of labor reduces earnings for natives as they compete for labor with immigrants. A significant increase in the number of immigrants, whether legal or illegal reduces wages for the natives. On the contrary, reducing legal immigration through strict immigration laws will inevitably increase the earnings for native workers in the country. Many people are migrating into US with the hope of a better life for themselves and their families. This because the country is seen as a land of opportunity.
Economic theory of labor market
Economic theory of labor market show that increasing the supply of a specific type of labor results in the decline of wage earnings in that particular job group. These job groups may be unskilled workers or skilled workers. Immigration leads to an increase in labor supply to a particular market. This reduces the wages of competing employees while increasing the wages of complementary employees. This influx of immigrants reduces the economic opportunities for native workers who are now faced with stiffer competition in the labor market. Immigrants are slowly taking over jobs from American natives because they’re cheap and hence preferred by many employers in the labor market.
Labor market consists of supply for labor, demand for labor, wages and employment levels. The labor demand and supply curve represent employers demand for labor and workers who want to supply labor respectively, and this determines the price of labor (wage) in the market. The equilibrium point where supply and demand for labor intersect is referred to as market clearing wage and this is point marked (x) in the graph. Markets with limited labor force, have higher wages than markets with plenty of workers. This is demonstrated in the graph below.
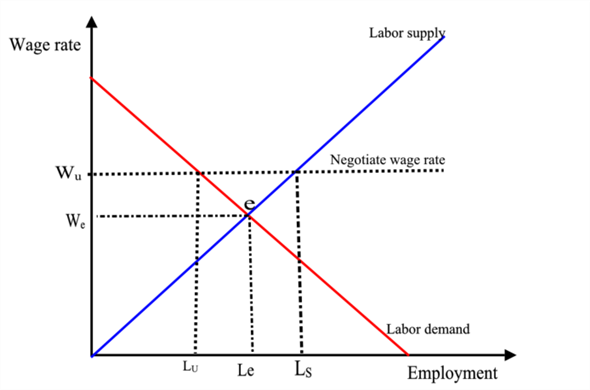
Explanation of the graph
The intersection between Lu and Wu is the market clearing wage, (x) and labor supply respectively. Any increase in the supply of labor from the initial Lu to Ls, (Lu <Ls) will shift the supply curve to the left from Si to Sii as shown in the figure above. This will consequently lead to reduced wages from Wu to We (Wu >We). Therefore, any increase in labor force reduces the price for labor in the market as more and more people compete for the little job vacancies in the labor market. Conversely, a decrease in labor force will push the supply curve to the right from Si to Siii as indicated by the figure. This will consequently push up the wage of workers.
Labor markets with large supply of labor than labor demand will result into lower wages for workers. Assuming the labor market presented by the graph shown above at equilibrium wage and labor at Wi and Li respectively. An influx in the number of immigrants will result in reduced wages similar to Wii and an increase in employment level similar to Lii at the new equilibrium level. Therefore, an increase in labor force should have a corresponding increase in the demand for labor for wage rate to remain constant.
Application to America labor market
Immigrants tend to cluster in a particular geographical location of the United States of America. Studies have shown that about 34 percent of working immigrants are clustered in three metropolitan areas of New York, Chicago and Los Angeles. Empirical studies on the impact of immigration on labor market have concentrated on this geographical clustering. A negative correlation of such studies could indicate that natives in these markets have lower wages than those in areas not penetrated by immigrants. This could show how immigrants have worsened the economic opportunities of competing native employees. However, most studies findings are clustered around zero implying that immigration has little or no impact on the labor market in those areas. This is because the flow of workers and jobs across cities of US tends to balance out economic condition across cities. The inter-city comparison could not reveal the effect of immigration on native wages hence the impact is felt across the national economy.
The impact of immigration on labor market could hence be measurable at the national level. Studies have been conducted by the department of labor, center for immigration and national academy for sciences at national level to establish the correlation between immigration and wages. They have concluded that indeed immigration has adverse effects on the wages and employment of natives as a result of increased competition for labor in the economy. The magnitude of the impact varies across different labor groups, race or ethnicity and the impact is more pronounced among the most underprivileged native minorities. The statistical findings indicate that immigration reduced annual earnings for a native born American by approximately $1, 7000 which is about 4 percent. The trend is even higher for unskilled labor force which faces the most competition from immigrants. The study further shows higher impact for black and Hispanic workers as compared to their white counterparts. This is because of direct competition between large portions of minorities with the immigrants (Camarota, 2002).
Challenges and exploitation of immigrants in the US
United States immigrants are faced with a number of challenges ranging from low pay and exploitation by US employers. Illegal and undocumented immigrants are engaged low paying jobs because they lack legal documents to take up well paying jobs. Most them work under unhealthy conditions and have no such benefits as pensions and health insurance. Most immigrants are lacking in the proficiency of English language and American culture and workplace norms and this hinders their access to good paying jobs.
Most immigrants are employed in seasonal and temporary jobs which are not protected by labor laws. Any attempt to participate in trade union drives is faced with intimidation from their employers that include reporting them to immigration and naturalization service.
There is need to improve the working conditions, wages and benefits for unskilled workers. These categories of work are essential for economic growth and development. Training of these workers is necessary for it promotes their productivity and improves career growth. Foundation can support appropriate strategic options geared towards improving the rights of unskilled workers being exploited in the labor markets. Efforts should be made towards educating children of immigrants for their long term career benefits and economic security. Leadership of immigrant and low income workers should be trained on how to protect their rights at places of work. Conducting research on immigrant and low wage employment is recommended to provide insights for public policy development. Foundations can also support policies and community efforts aimed at protecting immigrant workers against intimidation by their employers for engaging in union organized drives. Formation of legal services and litigation department to defend and advance the rights of low waged employees is essential (Camarota, 2002).
Impacts of illegal immigration on taxation
Analysis of costs and tax payments by illegal aliens indicate a net fiscal deficit on the federal budget. The cost imposed by illegal immigrants on federal government is higher than taxes they remit to government. This is because nearly two-third of them lack high school education and are employed in low income jobs which generate low taxes which cannot match the cost of social amenities. Giving amnesty to illegal aliens to begin paying taxes could significantly increase net fiscal deficit. The unskilled immigrants with legal status will qualify for government programs. The legalization of aliens could increase tax payments per household by 77% but will increase the average costs by 118% hence increased net fiscal deficit. That’s why immigrants with few schooling years are a drain to the fiscal budget (Camarota, 2002).
Conclusions
There is growing concern over the adverse effects of immigration on employment and wages on native born American. Illegal immigrants are a great challenge to the American economy. Majority of them are unskilled and are engaged in low paying jobs which cannot generate adequate taxation to offset their corresponding costs on fiscal budget. Although some employers prefer cheap labor offered by illegal immigrants, the cost of cheap labor is very high to the nation.
References
Camarota, S. A. (2002). Immigrants in the United States. A Snapshot of America’s Foreign-Born




